Ultrasonic cleaners rapidly vibrate a detergent or an enzyme bath up to 37,000 times per minute using sound waves. This vibration produces millions of tiny bubbles that impact your instruments’ surfaces with a comparatively high force, clearing them of unwelcome blood, saliva, and food particles. Dental ultrasonic cleaners are a very efficient way to clean dental instruments and restorations of all kinds of dirt. These powerful ultrasonic cleaners can even get into nooks and crannies where microscopic pollutants can hide. Read More…
Since 1972, Esma Inc. has been producing quality ultrasonic cleaners, as well as benchtop electropolishing equipment. Esma offers a unique and progressive approach to automating the ultrasonic cleaning process.

Since 1992 Telsonic Ultrasonics has been manufacturing ultrasonic cleaners such as compact cleaners and industrial tanks. As a specialist in ultrasonic technology, we offer innovative applications within the parts and optics industries and even chemical and pharmaceutical products. Our brand new facility houses cutting-edge technology where we strive to improve the quality of our products.
Great Lakes Finishing Equipment, Inc. is a full line supplier of aqueous and semi-aqueous ultrasonic cleaning equipment. Equipment includes benchtop cleaners, tank and generator series, immersible transducers, console systems and engineered systems. Our customers include defense, aerospace, medical, firearms and industrial.

Sonic Systems is a recognized leader in the design and manufacture of both ultrasonic cleaners as well as ultrasonic cleaning systems and components for a broad range of industries. We also offer aqueous cleaning equipment and systems.
More Dental Ultrasonic Cleaner Manufacturers
Dental ultrasonic cleaners manufacture products with frequencies between 40 KHz and 60 KHz. Ultrasonic cleaners are environmentally friendly because they don't use harsh chemicals to clean. Most ultrasonic cleaners used in dentistry labs are made of stainless steel. A built-in heater, thermostat, digital timer, and even touchscreen operation are features that some offer. Dental ultrasonic cleaners come in various sizes, from small bench-mounted models to huge cabinet-sized cleaners. Any manufacturer and model should come with a warranty, regardless of the purchase. Make sure to look into the supplier’s history before purchasing the dental ultrasonic cleaner.
Why Dental Instruments Need to be Ultrasonically Cleaned in Clinics
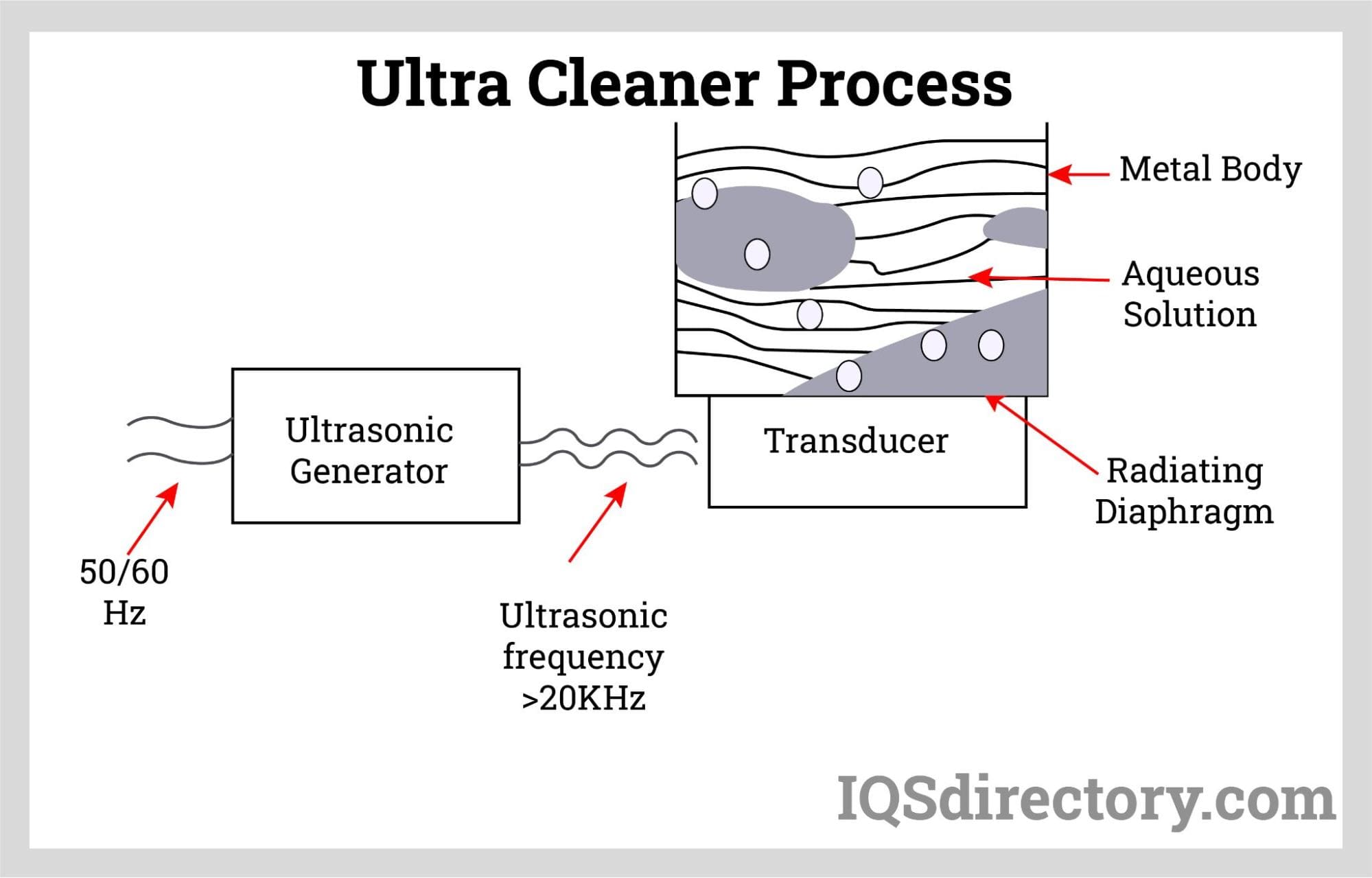
In an ultrasonic cleaning bath, billions of tiny suction bubbles are produced by ultrasonic energy, and when they come into contact with dental instruments, they explode violently. The procedure, known as cavitation, safely and swiftly blasts impurities from dental instruments' surfaces and carries them away. Dental instrument ultrasonic cleaners are quicker, safer, and more effective than mechanical washers or manually washing sharp and pointed tools. Only after a thorough ultrasonic cleaning, should dental instruments proceed to the second and third stages—disinfection or sterilization. The CDC claims that this is so because residues can hinder the inactivation of microorganisms and jeopardize following procedures.
Securing Lid
Any ultrasonic cleaner used to clean out dental equipment will most likely have a locking lid (Figure 3). Instruments can be removed from a cleaning cycle before they have finished processing for the required time, thanks to lids that can be opened throughout the cycle. Each instrument must be cleaned simultaneously to be considered repeatable; otherwise, human error may occur. In dentistry, ultrasonic cleaners shouldn't be opened without the cycle being nullified and a record being made stating that the instruments haven't been cleaned thoroughly enough.

Traceability and Validation
The ultrasonic cleaner, a device that meets the gold standard for decontaminating dental tools, should include a method of validating the cycle, just like the washer-disinfector and autoclave. Unfortunately, cycle validation is not a feature of many ultrasonic cleaners and a lot of dental offices still employ these antiquated devices. Newer machines made expressly for the dentistry sector often have an integrated printer, an SD card connector, and validation software that enables hard-copy and electronic cycle traceability. Dental nurses and decontamination specialists can be confident that the instruments have been thoroughly cleaned with the same intensity of ultrasonic cleaning activity thanks to the equipment that includes this information recording.
Choosing a Dental Ultrasonic Instrument Cleaner
When choosing a dental ultrasonic cleaner, several factors should be considered.
Cleaning Tank Volume
The tank's internal measurements are significant, but the mesh basket's dimensions—which hold the instruments—are even more crucial. Tank measurements are somewhat smaller than basket measurements. This is because instruments must be submerged entirely and must not come into contact with one another.
Ultrasonic Wavelength
For most dental instrument cleaning needs, a frequency of 37,000 cycles per second, or 37 kHz (lower frequencies), is suitable. However, when cleaning equipment with complicated or highly polished surfaces or difficult-to-remove impurities, multi-frequency units with higher frequencies are employed. To fight pollutants that are especially hard to remove, most manufacturers offer a modest fluctuation in ultrasonic frequency to encourage even more dispersion of cleaning energy.
Temperature Regulators
As was already said, a hot solution can bake pollutants onto surfaces. The solution is heated during the ultrasonic cavitation process. A cooling coil may be required to regulate solution temperature during prolonged cleaning cycles. Other cleaning jobs may benefit from a solution's capacity to be heated.
Timer
Using a timer, you can specify the length of the cleaning cycle.
Choosing the Proper Dental Ultrasonic Cleaner Manufacturer
To make sure you have the most productive outcome when purchasing dental ultrasonic cleaners from a dental ultrasonic cleaner manufacturer, it is important to compare at least 4 manufacturers using our dental ultrasonic cleaner directory. Each dental ultrasonic cleaner manufacturer has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the manufacturer for more information or request a quote. Review each dental ultrasonic cleaner company website using our patented website previewer to get an idea of what each company specializes in, and then use our simple RFQ to contact multiple dental ultrasonic cleaner companies with the same quote.







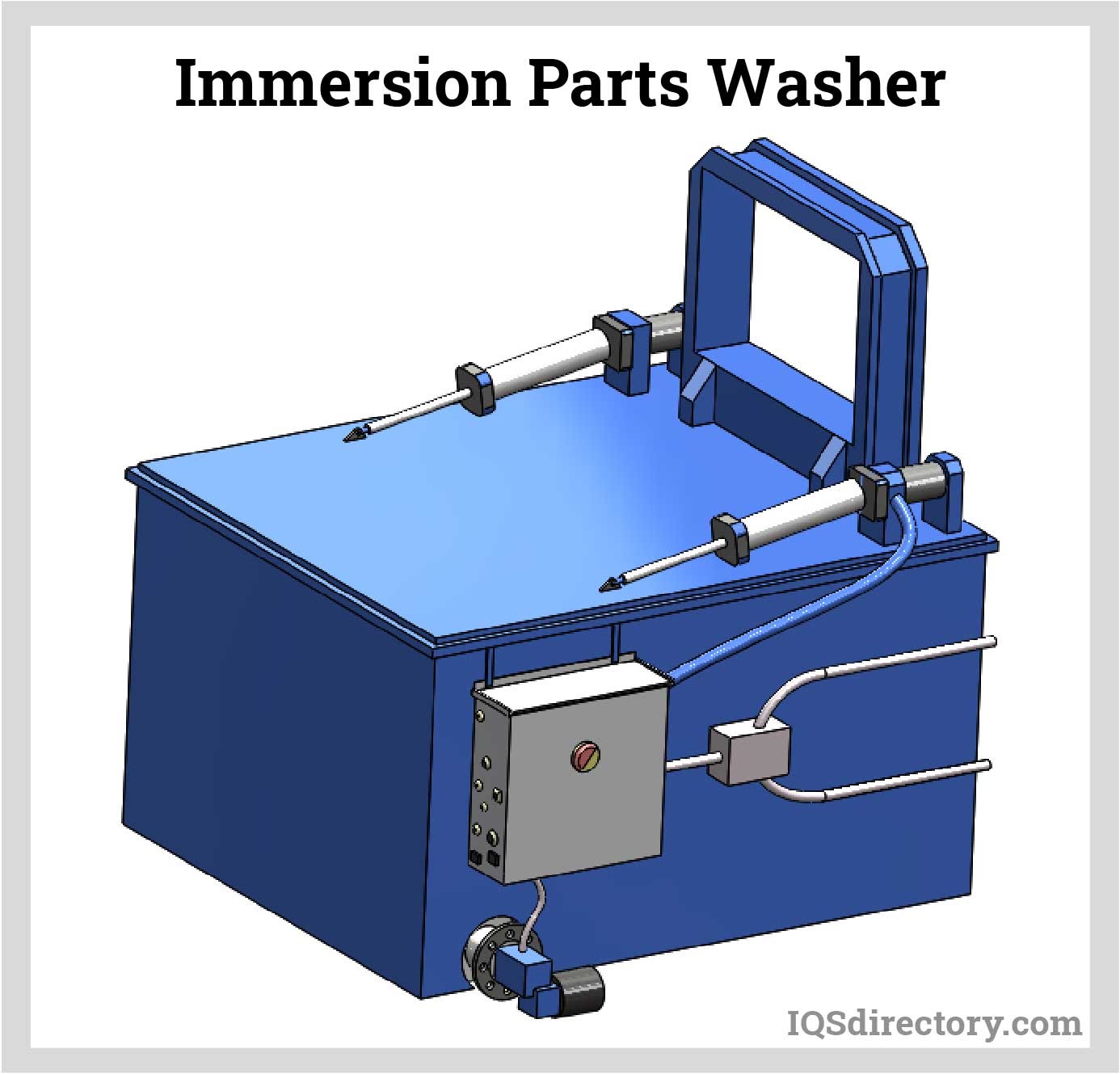
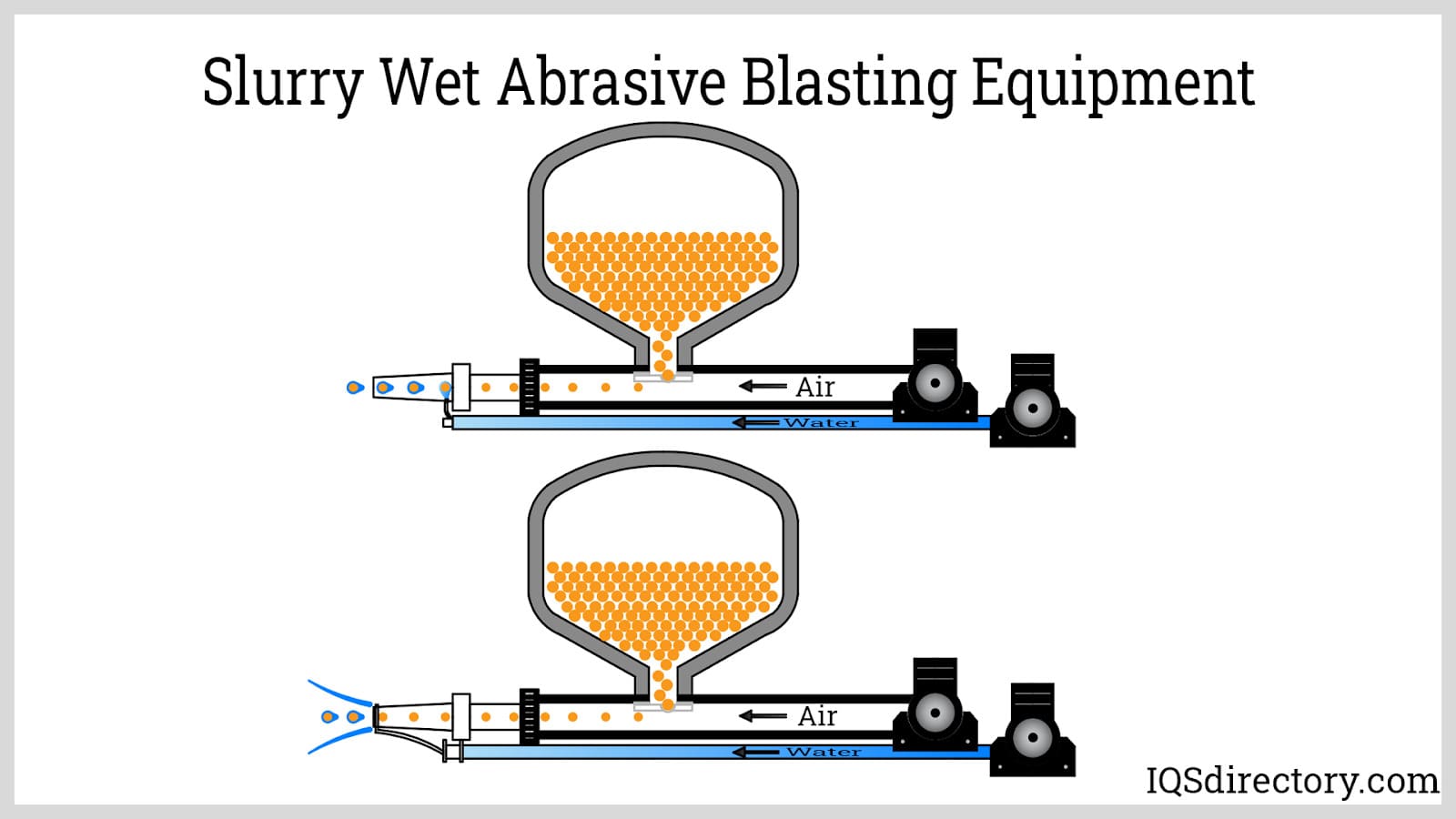
 Deburring Machinery
Deburring Machinery Industrial Parts Washers
Industrial Parts Washers Sandblast Equipment
Sandblast Equipment Ultrasonic Cleaners
Ultrasonic Cleaners Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services