The most crucial process in reprocessing a medical item is cleaning; effective disinfection and sterilization cannot be carried out without it. Ultrasonic cleaning can be both mild on delicate tools like microsurgical and ophthalmic devices and helpful for hard-to-reach locations on a device, such as fine serrations or box lock joints. Read More…
Since 1972, Esma Inc. has been producing quality ultrasonic cleaners, as well as benchtop electropolishing equipment. Esma offers a unique and progressive approach to automating the ultrasonic cleaning process.

Since 1992 Telsonic Ultrasonics has been manufacturing ultrasonic cleaners such as compact cleaners and industrial tanks. As a specialist in ultrasonic technology, we offer innovative applications within the parts and optics industries and even chemical and pharmaceutical products. Our brand new facility houses cutting-edge technology where we strive to improve the quality of our products.
Great Lakes Finishing Equipment, Inc. is a full line supplier of aqueous and semi-aqueous ultrasonic cleaning equipment. Equipment includes benchtop cleaners, tank and generator series, immersible transducers, console systems and engineered systems. Our customers include defense, aerospace, medical, firearms and industrial.

Sonic Systems is a recognized leader in the design and manufacture of both ultrasonic cleaners as well as ultrasonic cleaning systems and components for a broad range of industries. We also offer aqueous cleaning equipment and systems.
More Ultrasonic Washer Manufacturers
Ultrasonic Washers Working Principle
The agitation of a solution by mechanical vibrations during the ultrasonic cleaning procedure helps to remove dirt from the surfaces and, in some situations, the interior lumens of surgical instruments. The cavitation effect is a vacuum-like scrubbing action that removes soil from surfaces by causing minute implosions of bubbles to burst upon contact with surfaces. The bioburden is subsequently removed from the surface of the items submerged in the chamber.
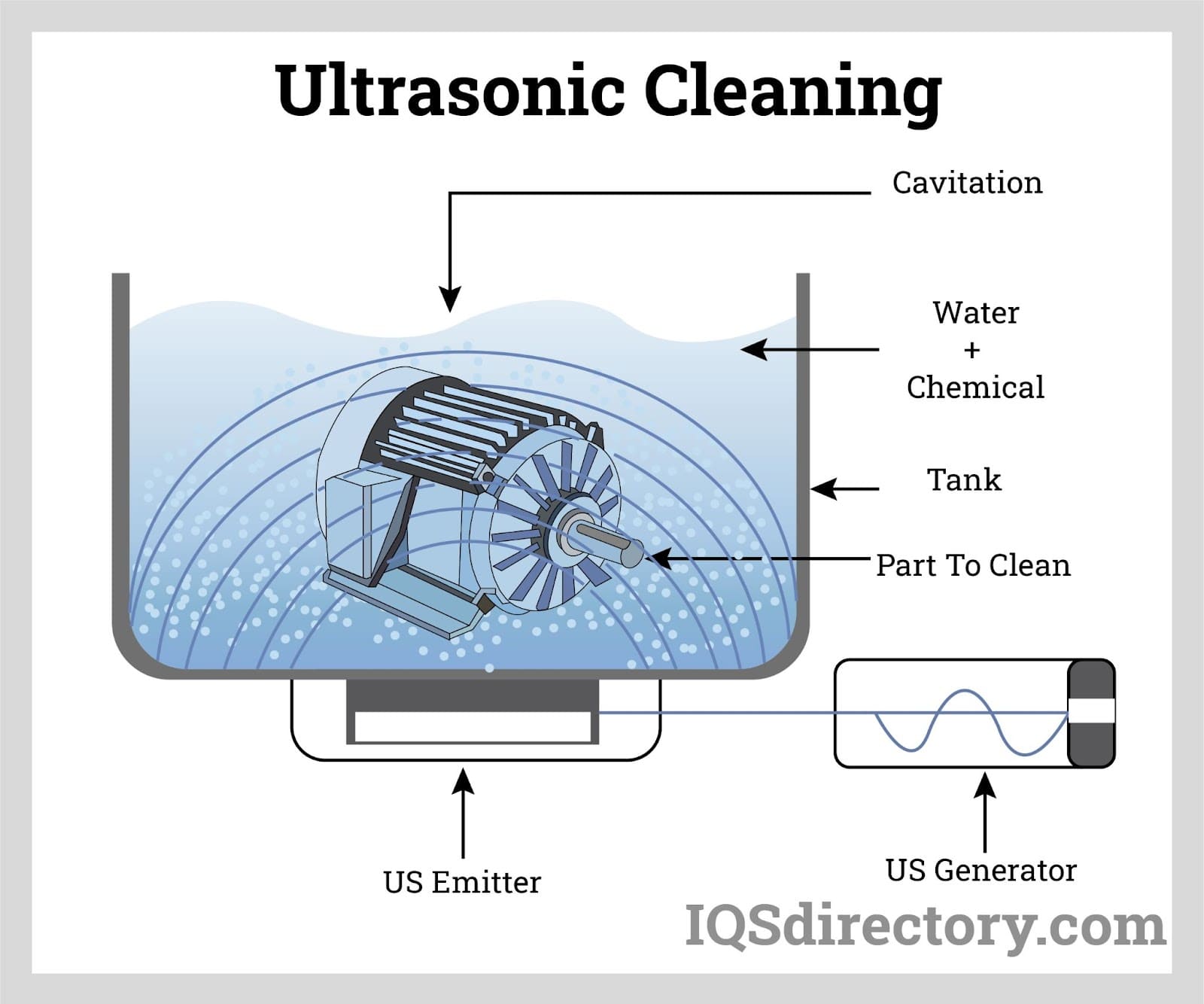
Utilizing a combination of these three parameters, ultrasonic cleaning systems effectively clean surfaces:
- Cavitation
- Flow/Sonic Irrigation
- Detergents
The proper combination of these criteria offers an effective cleaning method for delicate and challenging-to-clean medical devices, including Minimally Invasive Surgical (MIS) tools, laparoscopic devices, and robotic surgical attachments.
Cavitation And Ultrasonic Washers
The design of the ultrasonic system, particularly the ultrasonic frequency (measured in kilohertz, kHz) and power density, impact the cavitation process' effectiveness. Therefore, one should check with most popular device IFUs before purchasing an ultrasonic cleaner to ensure the frequency and power density are suitable for processing medical devices.

The design also impacts how the cavitation bubbles are produced. For instance, contemporary designs use ceramic transducers, which are kinder to gadgets than metal transducers used in older technology. Some systems install transducers near the tank's bottom, eliminating soil from instrument trays arranged in a single layer. This is because the instrument surfaces on the first, closest tray that the ultrasonic waves will encounter will be more effectively imploded by the cavitation than the instrument surfaces on the second or third tray because the ultrasonic waves are rising from the bottom. However, large ultrasonic cleaners mount transducers to the tank's sidewalls, making it possible to thoroughly clean multiple levels of trays.
Flow and Sonic Irrigation
Some ultrasonic cleaners also have sonic irrigation, often known as flow. The internal channels of lumened or cannulated devices can be cleaned more effectively with solution flow, while pressured flow can enhance mechanical cleaning.
Certain sophisticated surgical instrument cleaning validations call for a minimum pressure for the flow, which also serves as a crucial parameter to guarantee that the instruments' internal bioburden is cleared. However, a high-pressure flow combined with the correct ultrasonic cavitation does ensure that complex and sophisticated instruments are properly reprocessed.
Detergents For Ultrasonic Cleaning
A crucial step in the ultrasonic cleaning process is selecting the cleaning chemical. In addition, these detergent-based products must be able to clean, work with various water types, not hurt the device while guarding against long-term damage, and be simple to rinse and work with the ultrasonic cleaning system.

Ultrasonic Washers on Surgical Equipment
Today's surgical environment includes several pieces of equipment with detailed, delicate, and complex designs. This equipment, from delicate ophthalmic and laparoscopic devices to heavy orthopedic instruments, can be safely and effectively cleaned using ultrasonics. Without endangering a complex gadget, an ultrasonic cleaning procedure scours small crevices, uneven surfaces, and interior channels. The purpose of ultrasonic washers is to remove stubborn dirt from the surface and lumens of instruments while achieving consistent cleaning results throughout the washer chamber.
Ultrasonic Washers Recommendation
Installation, use, and maintenance of ultrasonic cleaning equipment should be done in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations. This will involve following suggested preventative and routine maintenance procedures and using certain cleaning detergents.
To use ultrasonic cleaning equipment safely and effectively, the following suggestions are made:
- Before using an ultrasonic cleaner to clean the instrument, gross soil should be removed (pre-cleaned), and the lumens should be brushed or flushed.
- Chemicals for cleaning surgical instruments should be created for use with ultrasonic systems.
- Before processing devices, it is typically advised to degas freshly prepared cleaning solution while adhering to the manufacturer's instructions.
- To verify compatibility, refer to the device's usage instructions. Due to the possibility of causing damage to devise components, some devices/construction materials (such as rubber or some types of adhesives on optical components) are not advised for sonication. In addition, devices made of stainless steel and other materials may not be compatible with metals like brass, copper, aluminum, or chrome plate.
- It is important to periodically switch out cleaning solutions, ideally after each usage and before processing ophthalmology instruments.
- The sonic unit is advised to undergo periodic verification testing to ensure that the cleaning procedure operates as intended. Daily and recurring service maintenance and the usage of a cleaning verification indicator, such as the VERIFY Ultrasonic Indicator, are all included.
Combining all these factors can achieve an ideal device cleaning procedure in ultrasonic cleaning systems.
Choosing the Correct Ultrasonic Washer Company
To make sure you have the most positive outcome when purchasing ultrasonic washers from an ultrasonic washer company, it is important to compare at least 5 companies using our ultrasonic washer directory. Each ultrasonic washer company has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the company for more information or request a quote. Review each ultrasonic washer business website using our proprietary website previewer to get an idea of what each business specializes in and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple ultrasonic washer companies with the same quote.







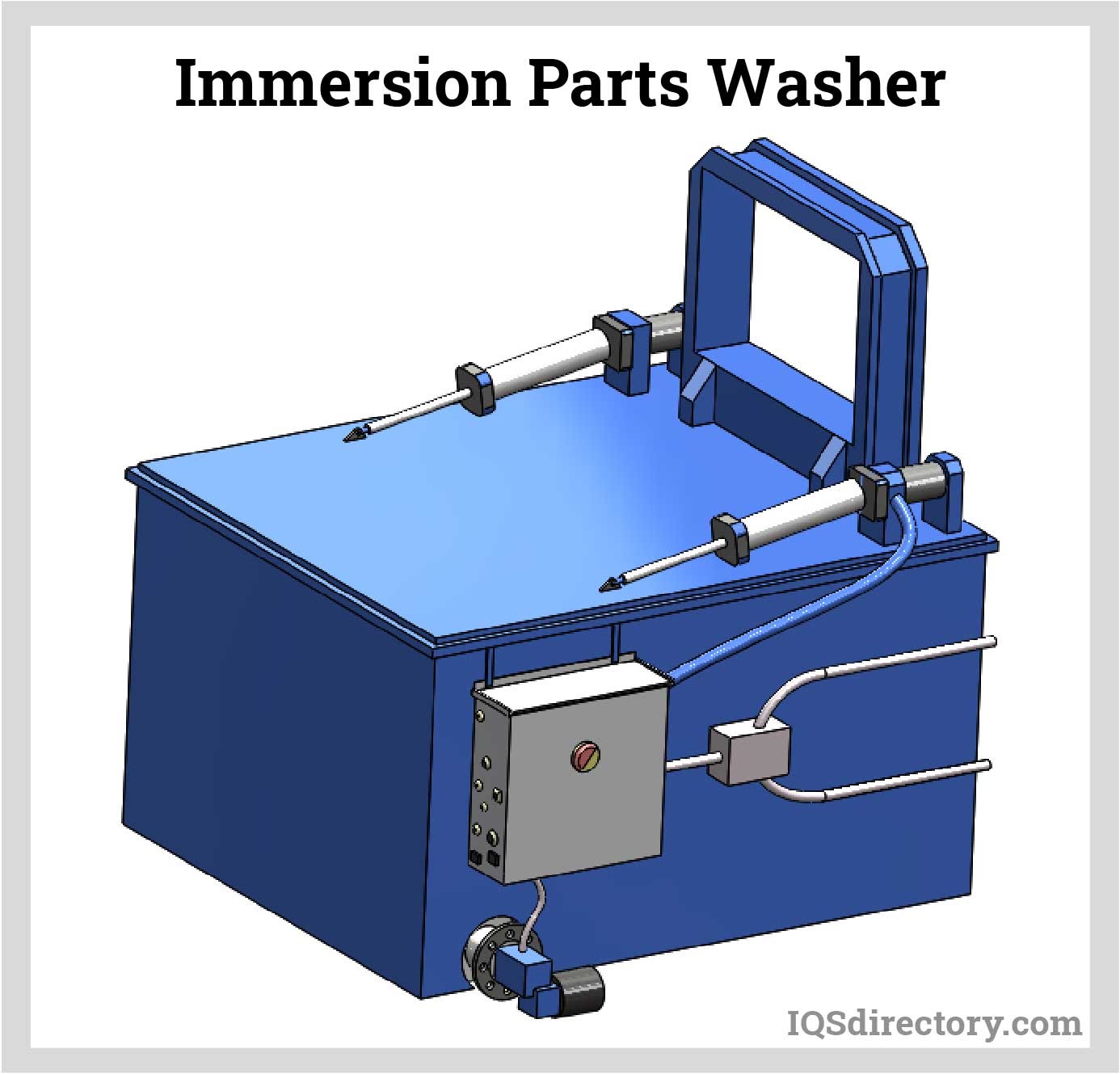
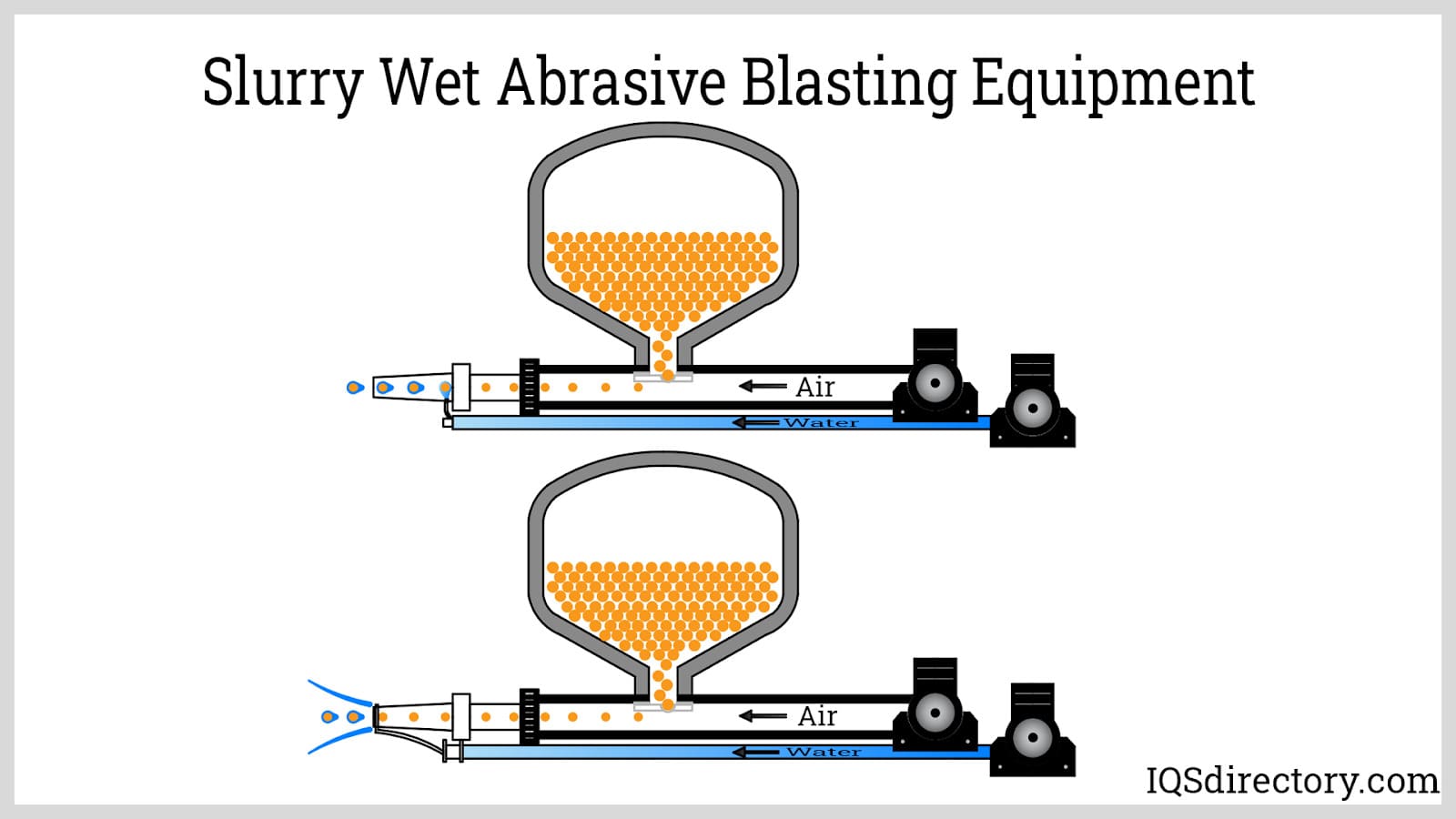
 Deburring Machinery
Deburring Machinery Industrial Parts Washers
Industrial Parts Washers Sandblast Equipment
Sandblast Equipment Ultrasonic Cleaners
Ultrasonic Cleaners Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services